Reproduction in Lower Animals
Reproduction in Lower Animals: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Regeneration in Planaria, Sexual Reproduction in Organisms, Gemmule in Sponges and Budding in Hydraetc.
Important Questions on Reproduction in Lower Animals
Reproduction:
One advantage of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction is that it helps species to survive over long evolutionary time. This is because sexual reproduction produces:
Difference between spores and gemmules:
What is the function of pinacocytes in a gemmule?
Which of the following multiply by the process of fragmentation?
Which of the following organism's growth is synonymous with reproduction?
Define gemmule.
Gemmule helps in perennation as well as dispersal.
In Hydra, budding is usually formed in the upper part of the body.
Write the process of budding in hydra.
How is sexual reproduction formed?
What are examples of organisms that reproduce sexually?
Reproduction is synonymous with growth in:
In which of the following organisms, reproduction is not synonymous with growth?
Reproduction
Which of the following is incorrect for reproduction?
Mark the incorrect pair.
Consider the following statements and select the correct option.
(a) Growth cannot be taken as defining property of living organisms.
(b) Reproduction is an exclusive defining characteristic of living organisms.
(c) Metabolism can be regarded as defining feature of all living organisms.
(d) All living organisms are self-conscious.
Which type of asexual reproduction is observed in Hydra?
Look at the given figure and find out the statements wrong regarding the gemmule formation,
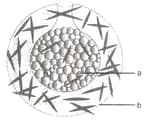
A. refers to an archeocyte and a refers to a gemmule
B. Gemmule formation takes place only in marine sponges
C. On germination, each gemmule gives rise to many offsprings
D. Gemmule formation is a kind of spore formation
